2021. 10. 8. 17:14ㆍ개발
GET
controller class와 user 클래스로 구성
package com.example.emp;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class Controller {
@GetMapping("/user/info")
public User getUserInfo() {
User user = new User();
user.setId("tom123");
user.setEmail("as@naver.com");
user.setName("tom jackson");
return user;
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}get 방식요청.. GetMapping을 사용 괄호 안에(/user/info) url 주소를 사용 맵핑을 한다.
package com.example.emp;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class User {
private String id;
private String name;
private String email;
}User 클래스 게터 세터 메서드 + tostring 메서드로 구성
lombok을 이용하여서 하나하나 만들 필요 없이 annotation을 줘서 구성할 수 있다.
@data 하나만 써도 전부 다 사용 가능
sts4 맥북 환경에서의 lombok환경설정에 꾀나 애를 먹었지만 말이다.. 시간이 되면 따로 다루어보자
결과

get방식으로 요청하고 결과물을 얻었다.
POST
dto 는 User로 동일하게 설정
PostController 만 만들어서 진행
목표 : get방식으로 얻어진 데이터를 클라이언트측에서 수정해서 서버로 보내보자 !
package com.example.emp;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostController {
@PostMapping("/post")
public void post2(@RequestBody User us) {
System.out.println(us);
System.out.println(us);
System.out.println(us);
}
}@RequestBody 의 역할은 ?
-> @RequestBody 어노테이션이란?
- HTTP 요청의 body 내용을 자바 객체로 매핑하는 역할을 합니다.
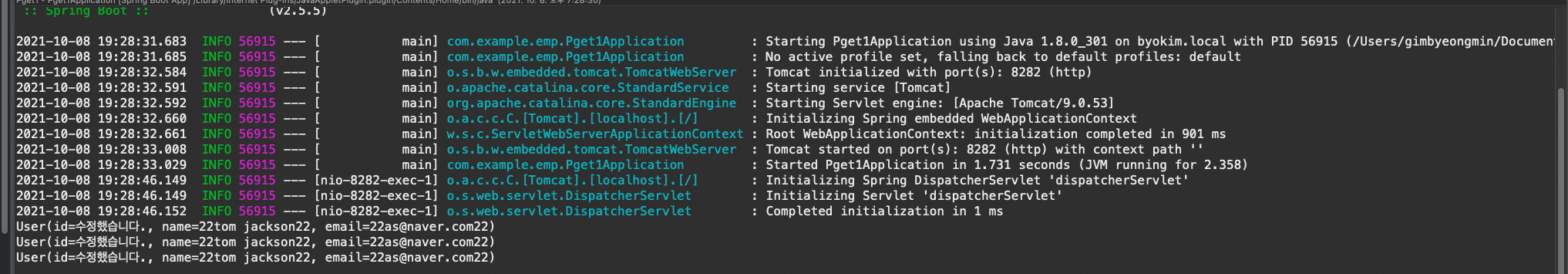
결과
PUT
dto 는 User로 동일하게 설정
PutController 만 만들어서 진행
목표 : POST 되어진 항목을 put으로 바꿔보자
package com.example.emp;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/PUT")
public class PutController {
@PutMapping("/user/info")
public User put(@RequestBody User us) {
System.out.println(us);
return us;
}
}결과

서버에 put으로 json을 보내고 post 랑은 다르게 get 처럼 body에 나옴 = > 클라이언트 측에 표시
PATCH
delete랑 구조비슷
package com.example.emp;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PatchMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/PATCH")
public class PatchController {
@PatchMapping("/user/{id}") //user/tom123?email=as@naver.com
public void patch(@PathVariable String id,
@RequestParam String email) {
User us = new User();
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(email);
}
}
하면됨 근데 항목하나만 수정하면 다른값은 null 값으로 바뀌는데 이건 어떻함 ?
DELETE
dto 는 User로 동일하게 설정
DeleteController 만 만들어서 진행
목표 : 처음 GET을 한 tom123을 지워보자
package com.example.emp;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/del")
public class DeleteController {
// delete, members/tom123?email=as@naver.com
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable String id,
@RequestParam String email) {
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(email);
// delete - >리소스 삭제 200 ok,
}
}



@PathVariable @RequestParam 차이설명
https://willbesoon.tistory.com/102
@RequestParam @PathVariable 차이점 비교
웹 개발에서는 http의 비연결성으로 인해 데이터를 전달해줄 여러가지 방법들이 있어왔습니다. 예전에는 쿠키도 있었고 세션도 있었고 여러가지 방법들이 있었는데요. 스프링에서도 두 가지의
willbesoon.tistory.com
보면은 Patch 랑 delete 만 dto 접근방식이 다른데 get 은 자바객체에서 받아오는거라 생각해서 @RequestBody 안쓴다고 하는데
post 와 put은 씀 근데 patch 랑 delete는 @PathVariable @RequestParam 이걸써서 접근함 차이점이랑 효과는 ?
그리고 지금 patch 연습하는데 자꾸 바꾸고 나서 null값뜸 ; 어떻게 해결 ?
'개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 회사소개 정리 (0) | 2021.11.11 |
|---|---|
| REST-API 개념정리 (0) | 2021.10.08 |
| 팀 프로젝트 정리 (0) | 2021.10.07 |
| 2021-10-7(목) (0) | 2021.10.07 |
| 2021-10-06 기록 (0) | 2021.10.06 |